Whats Bitcoin: A Guide to the Revolutionary Digital Currency
What’s bitcoins – What’s Bitcoin? It’s not just a cryptocurrency; it’s a revolutionary digital currency that has taken the world by storm. Its decentralized nature and underlying blockchain technology have made it a force to be reckoned with, disrupting traditional financial systems and opening up new possibilities for individuals and businesses alike.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of Bitcoin, exploring its concept, characteristics, value, mining process, security, and regulatory landscape. We’ll also uncover its potential future developments and applications, providing you with a thorough understanding of this transformative technology.
Overview of Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, created in 2009 by an unknown individual or group using the name Satoshi Nakamoto. It is a peer-to-peer payment system that operates without a central authority or intermediaries, relying instead on a distributed network of computers to verify and record transactions.
The underlying technology behind Bitcoin is called blockchain, a distributed ledger that records every transaction made on the network. Each block in the blockchain contains a hash of the previous block, creating an immutable chain of records. This makes it extremely difficult to tamper with or alter transactions, providing a high level of security.
Decentralized Nature
Unlike traditional fiat currencies issued by central banks, Bitcoin is not controlled by any single entity. Instead, it is maintained by a network of computers spread across the globe, making it resistant to censorship or manipulation by governments or financial institutions.
Uses of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has gained widespread adoption in various industries, including:
- Payments:Bitcoin can be used to send and receive payments globally, with low transaction fees and fast processing times.
- Investment:Bitcoin has become a popular investment asset, with its value fluctuating based on market demand and supply.
- Remittances:Bitcoin can facilitate cross-border remittances, offering lower fees and faster delivery compared to traditional methods.
- Supply Chain Management:Blockchain technology, underlying Bitcoin, can enhance supply chain transparency and efficiency.
Characteristics of Bitcoin
Bitcoin, a decentralized digital currency, possesses unique characteristics that distinguish it from traditional fiat currencies. These characteristics play a pivotal role in shaping its value, security, and usability.
Scarcity
Bitcoin’s scarcity stems from its limited supply, capped at 21 million coins. This predetermined supply creates a sense of scarcity, which can drive up its value in times of high demand.
Advantages:Preserves value over time, provides a hedge against inflation.
Disadvantages:Limits the potential for future growth, could lead to volatility.
Divisibility
Bitcoin can be divided into smaller units, known as satoshis. This divisibility enables users to make precise transactions, regardless of the amount.
Advantages:Facilitates microtransactions, enhances accessibility.
Disadvantages:May increase transaction fees, potential for confusion due to multiple units.
Immutability
Once a Bitcoin transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes immutable and cannot be reversed. This ensures the integrity and security of the network.
Advantages:Prevents fraud, provides transparency, enhances trust.
Disadvantages:Limits flexibility, can be challenging to recover lost or stolen funds.
Compared to traditional currencies, Bitcoin’s scarcity, divisibility, and immutability introduce both advantages and disadvantages. These characteristics contribute to its unique value proposition and shape its potential as a financial instrument.
Value and Price of Bitcoin: What’s Bitcoins
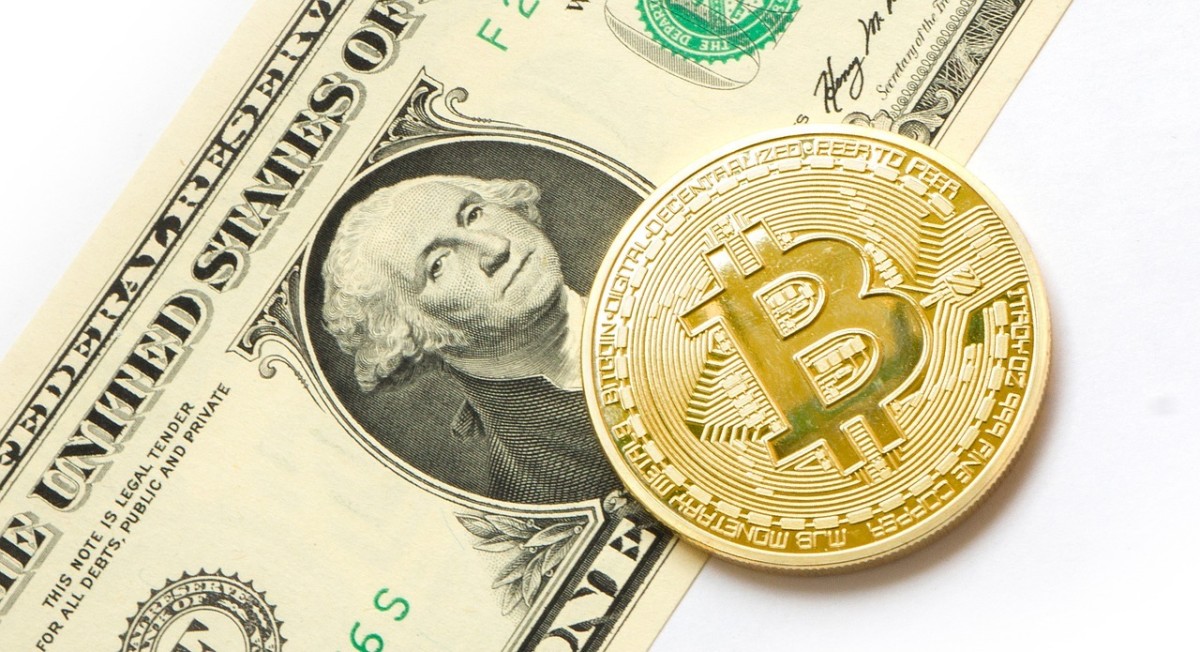

Bitcoin’s value is determined by various factors, including supply and demand, market sentiment, regulations, and technological advancements. Its price has experienced significant fluctuations since its inception, influenced by these factors and speculative trading.
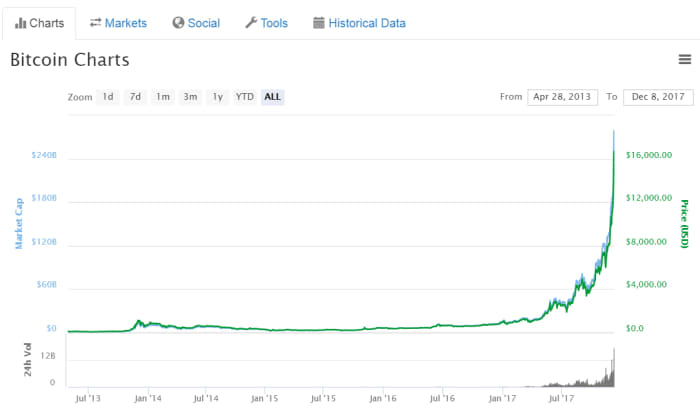
Historical Price Fluctuations, What’s bitcoins
- Early Growth (2009-2013):Bitcoin’s price gradually increased as awareness and adoption grew.
- First Bubble (2013-2014):The price surged to $1,200, driven by speculation and FOMO.
- Crash and Recovery (2014-2017):The price plummeted to $200 but later recovered.
- Second Bubble (2017-2018):The price reached an all-time high of $20,000, fueled by institutional interest and retail investors.
- Bear Market (2018-2020):The price declined significantly, stabilizing around $5,000.
- Third Bubble (2020-2021):The price surged to a new all-time high of $64,000, driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and institutional adoption.
- Current Bear Market (2022-Present):The price has been declining due to macroeconomic factors, geopolitical tensions, and regulatory concerns.
Potential Factors Affecting Future Price
- Institutional Adoption:Increased adoption by financial institutions and corporations could drive demand and increase the price.
- Regulatory Landscape:Clear and favorable regulations could enhance trust and stability, potentially boosting the price.
- Technological Developments:Advancements in blockchain technology, such as the Lightning Network, could improve scalability and adoption, potentially increasing the price.
- Economic Conditions:Economic uncertainty or inflation could drive investors to seek alternative assets like Bitcoin, potentially increasing its price.
- Market Sentiment:Positive market sentiment and bullish predictions could attract new investors and drive the price higher.
Mining and Transaction Process

Bitcoin mining is the process of verifying and adding new transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain. It involves solving complex mathematical problems, which require significant computational power. Miners who successfully solve these problems are rewarded with newly created Bitcoins. Mining is essential for the security and integrity of the Bitcoin network, as it ensures that transactions are processed and recorded accurately and securely.
Steps Involved in a Bitcoin Transaction
When a Bitcoin transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to the Bitcoin network. Miners collect these transactions and group them into blocks. Once a block is full, miners compete to solve the complex mathematical problem associated with it. The first miner to solve the problem successfully adds the block to the blockchain, which is a public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions.
The miner who adds the block is rewarded with newly created Bitcoins and transaction fees.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees are optional payments made to miners to incentivize them to process transactions quickly. The amount of the transaction fee is determined by the size of the transaction and the current demand for block space. Miners can choose to prioritize transactions with higher fees, which can result in faster processing times.
Last Word
As we look towards the future of Bitcoin, it’s clear that it has the potential to revolutionize the global financial system. Its decentralized nature, immutability, and scarcity make it a compelling alternative to traditional currencies, offering greater transparency, security, and control.
While challenges remain, the future of Bitcoin looks bright, with continued innovation and adoption promising to unlock its full potential.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the purpose of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows for secure, peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which is maintained by a network of computers. These transactions are verified and secured through a process called mining.
What are the advantages of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin offers several advantages over traditional currencies, including decentralization, transparency, security, and the potential for anonymity.
What are the risks of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a volatile asset, and its value can fluctuate significantly. Additionally, there are security risks associated with storing and transacting Bitcoin.
What is the future of Bitcoin?
The future of Bitcoin is uncertain, but it has the potential to revolutionize the global financial system. Continued innovation and adoption could unlock its full potential.